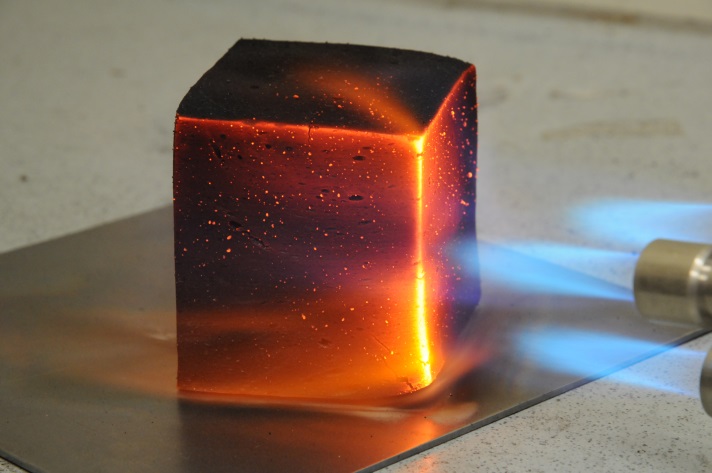
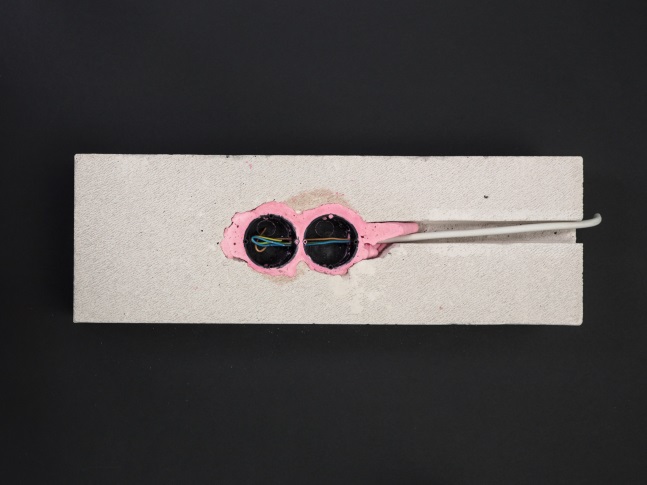
Novel ceramizing and foam-forming coating materials and high-temperature insulation materials are developed for fire protection. Protection from fire and heat is provided by intumescent, ablative, ceramizing and cooling processes. Intumescent coatings swell at increased temperatures and form an insulating foam which protects thesubstrate. In addition, endothermic reactions can generate a cooling effect.
In the field of flame protection, established halogen-containing flame retardants are increasingly being replaced by halogen-free alternatives. Besides their performance, the effects of these substances on the material properties also play a decisive role. Current research topics include halogen-free flame retardants for epoxy resin systems which have minimal influence on the glass transition temperature.
 Fraunhofer Institute for Chemical Technology ICT
Fraunhofer Institute for Chemical Technology ICT